Table of Contents
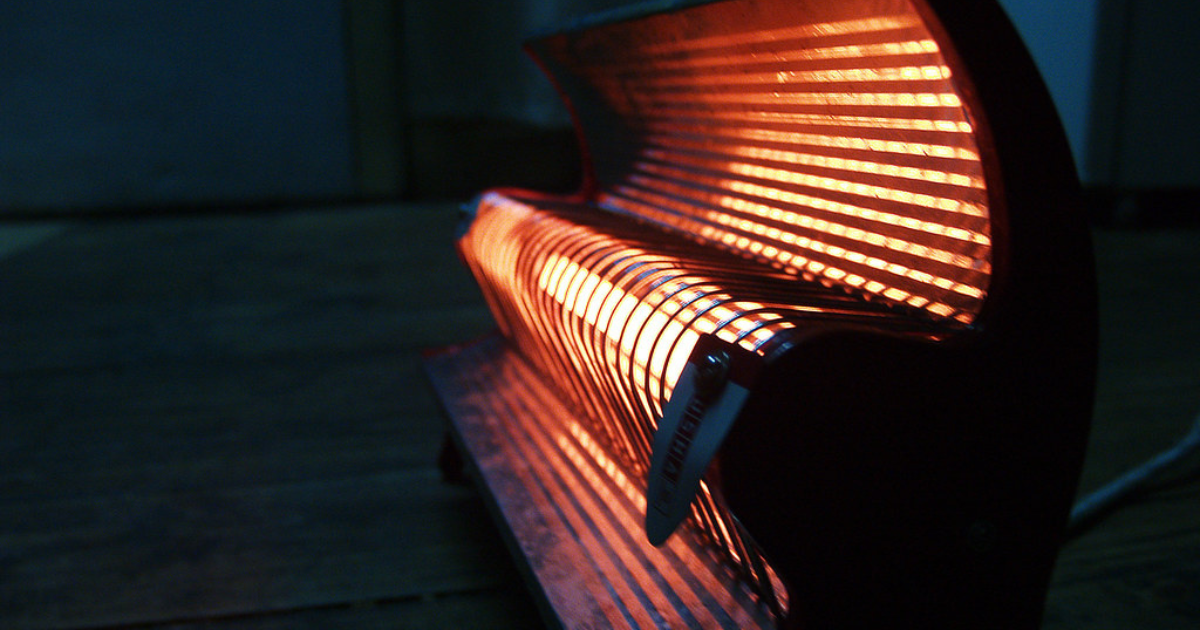
As winter blankets us in its chill, room heaters become our allies in the battle against the cold. However, their cozy warmth might come at a price, especially when used during the night. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of room heatersand try to understand Why Room Heaters Are Not Safe In Night. , their operation, safety features, and the potential risks associated with nighttime use.
Introduction
A. Importance of Room Heaters
Room heaters have become indispensable during the colder months, providing instant warmth and comfort. Their compact size and efficiency make them a popular choice for heating individual spaces.
B. Nighttime Safety Concerns
While room heaters offer respite from the cold, using them at night raises safety concerns. Understanding these risks is crucial for ensuring a cozy night’s sleep without compromising safety.

II. Understanding Room Heaters
A. Types of Room Heaters
1. Convection Heaters
Convection heaters circulate warm air throughout the room, making them effective for larger spaces.
2. Radiant Heaters
Radiant heaters emit infrared radiation, directly heating objects and people in their line of sight.
3. Ceramic Heaters
Ceramic heaters use ceramic plates to heat the air, offering a balance between convection and radiant heating.
B. How Room Heaters Work
Room heaters operate on the principle of converting electrical energy into heat. Understanding their functioning is essential for safe usage.
III. Safety Features During Operation
A. Automatic Shut-off
Modern heaters often come equipped with automatic shut-off features to prevent overheating.
B. Overheat Protection
Built-in sensors detect excessive heat and trigger automatic shut-off to prevent fires.
C. Tip-Over Switch
This safety feature ensures that the heater turns off if accidentally knocked over, reducing the risk of accidents.
IV. Why Room Heaters Are Not Safe In Night.
A. Lack of Supervision
Nighttime use often means heaters operate in unattended rooms, increasing the risk of accidents.
B. Increased Fire Hazards
Extended operation during the night can lead to overheating and, in extreme cases, fires.
C. Health Implications
Prolonged exposure to dry, heated air can affect respiratory health, especially during sleep.
V. Alternatives for Safe Heating at Night
A. Electric Blankets
Electric blankets offer a safer alternative, providing localized warmth without the risks associated with room heaters.
B. Micathermic Heaters
Micathermic heaters combine the benefits of convection and radiant heating, offering a safe option for nighttime use.
C. Oil-Filled Radiators
Oil-filled radiators provide a steady, safe heat source, making them suitable for overnight heating.
VI. Tips for Safe Room Heater Use
A. Regular Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance ensures that heaters operate efficiently and safely.
B. Proper Ventilation
Adequate ventilation prevents the accumulation of carbon monoxide, a byproduct of combustion in some heaters.
C. Ideal Placement
Placing heaters away from combustible materials and ensuring proper clearance reduces the risk of fires.
VII. Real-Life Incidents and Safety Lessons
A. Case Studies
Examining real-life incidents helps extract valuable safety lessons for users.
B. Extracting Key Safety Practices
Analyzing incidents highlights the importance of adhering to safety guidelines and using heaters responsibly.
VIII. Myth Busting: Common Misconceptions
A. Debunking Nighttime Safety Myths
Addressing common misconceptions about nighttime heater use provides clarity to users.
B. Educating Users
Educating users about safe practices fosters a responsible approach to room heater use.
IX. Balancing Warmth and Safety
A. Temperature Settings
Moderating temperature settings ensures comfort without compromising safety.
B. Duration of Use
Limiting the duration of heater operation reduces the risks associated with prolonged use.

X. The Impact on Energy Consumption
A. Efficient Heating Practices
Implementing energy-efficient heating practices benefits both the environment and the user.
B. Cost-Effective Alternatives
Exploring alternative heating options can provide cost-effective solutions without compromising safety.
XI. User Reviews and Experiences
A. Positive Experiences
Understanding positive user experiences helps identify room heaters that prioritize safety.
B. Learning from Negative Experiences
Analyzing negative experiences guides users away from potential safety hazards.
XII. Safety Standards and Regulations
A. Industry Guidelines
Adhering to industry guidelines ensures that manufacturers prioritize safety in their designs.
B. Government Regulations
Government regulations play a crucial role in setting safety standards for room heaters, protecting consumers.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Recap of Safety Measures
Summarizing safety measures reinforces the importance of responsible room heater use.
B. Responsible Room Heater Use
Ensuring nighttime safety involves a combination of user awareness, proper maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines.
XIV. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A. Are all room heaters unsafe at night?
Not necessarily. Choosing heaters with advanced safety features and following guidelines can mitigate risks.
B. What should I do if my room heater malfunctions during the night?
Immediately turn it off and unplug it. Seek professional assistance for repairs.
C. Can children and pets be in the room with a heater on?
It’s advisable to keep children and pets away from operating heaters to prevent accidents.
D. Are there any specific fire-resistant materials recommended for heater placement?
Using non-flammable materials around the heater reduces the risk of fires. Opt for metal or ceramic surfaces.
E. How often should I schedule maintenance for my room heater?
Regular maintenance, at least once a year, ensures optimal performance and safety.